11.33 Faceted Location Scatter Plot
REVIEW
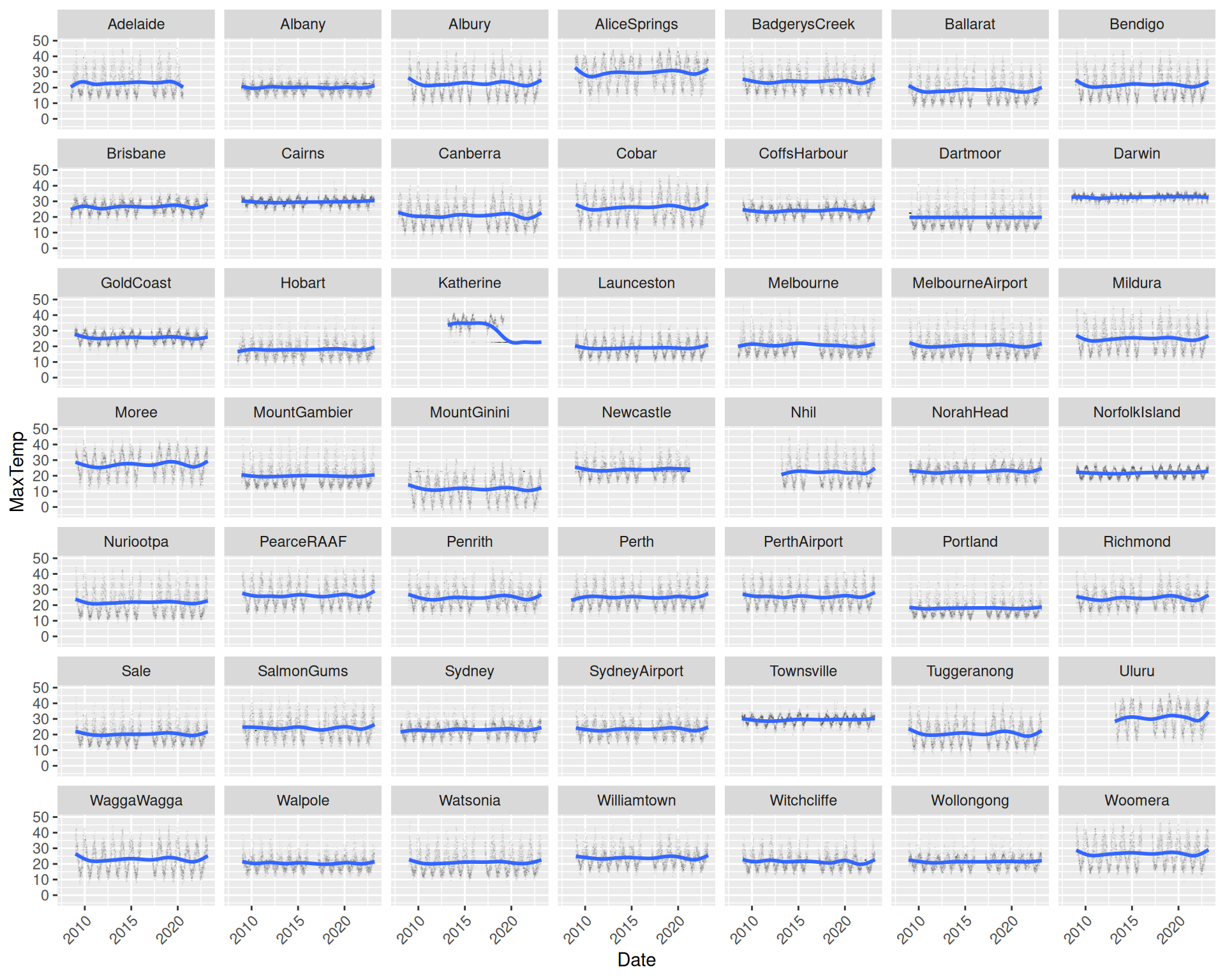
ds %>%
ggplot(aes(x=date, y=max_temp)) +
geom_point(alpha=0.05, shape=".") +
geom_smooth(method="gam", formula=y~s(x, bs="cs")) +
facet_wrap(~location) +
theme(axis.text.x=element_text(angle=45, hjust=1)) +
labs(x=vnames["date"], y=vnames["max_temp"])Partitioning the dataset by a categoric variable reduces the blob
effect for big data. The plot uses location as the faceted
variable to separately plot each location’s maximum temperature over
time. Notice the seasonal effect across all plots, some with quite
different patterns.
The plot uses ggplot2::facet_wrap() to separately plot each
location. Using ggplot2::geom_point() with alpha=
reduces the effect of overlaid points as does using smaller dots on
the plots by way of shape=. Together this works to
de-clutter the plot and improves the presentation with an emphasis on
the patterns. The x-axis tick labels are rotated \(45^\circ\) using
angle=45 within ggplot2::element_text() to
avoid the labels overlapping. The hjust=1 forces
the labels to be right justified.
Your donation will support ongoing availability and give you access to the PDF version of this book. Desktop Survival Guides include Data Science, GNU/Linux, and MLHub. Books available on Amazon include Data Mining with Rattle and Essentials of Data Science. Popular open source software includes rattle, wajig, and mlhub. Hosted by Togaware, a pioneer of free and open source software since 1984. Copyright © 1995-2022 Graham.Williams@togaware.com Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0
